Android是基于Linux 2.6 内核的系统,所以理论上Linux OS可以运行的脚本语言,给予相应的运行库,在Android也可以运行。
在Android手机上编写并运行Lua脚本
利用开源项目SL4A ( Scripting Layer for Android 项目地址:http://code.google.com/p/android-scripting/ ) ,可以快速在Android手机上搭建各种脚本运行环境。目前SL4A支持 Python, Perl, JRuby, Lua, BeanShell, JavaScript, Tcl, shell 等脚本语言 。
1、下载并安装SL4A运行环境
最新 sl4a_r6.apk 下载地址:http://android-scripting.googlecode.com/files/sl4a_r6.apk
这个应用提供了各种脚本的运行环境,通过拆APK可以看到应用内嵌了两个.so动态链接库。其中一个是ConnectBot的库,另一个是7.9K大小的脚本执行库,但显然不是脚本语言解析库。具体关于SL4A的原理,可以参考博文:《SL4A 之实现原理解析》
2、下载 Lua for android 支持
lua_for_android_r1.apk 下载地址:http://android-scripting.googlecode.com/files/lua_for_android_r1.apk
3、运行Lua for android ,它将从网络下载一些Lua脚本Demo。这些例子在SL4A中运行。
使用SL4A可以在Android手机上直接运行Lua等脚本。
其它脚本语言,可以到 http://code.google.com/p/android-scripting/downloads/list 下载相应的APK。
在Android项目中使用Lua脚本
SL4A 交互式的脚本运行方式不适合在Android项目中使用。如果你的项目要使用Lua脚本,就需要将Lua嵌入到Android项目中。
在Android项目中使用Lua,需要两个步骤:
1、加载Lua脚本解析引擎。
2、以Native API方式调用引擎接口
直接以JNI方式调用Lua解析引擎的接口十分麻烦,开源项目LuaJava对这些JNI接口进行了很好的封装。
AndroLua是一个包含了LuaJava的Android平台的Lua解析器,它提供一系列映射到Lua C实现函数的Java接口。
1、用Git将项目克隆到Eclipse的工作目录中
git clone https://github.com/mkottman/AndroLua.git
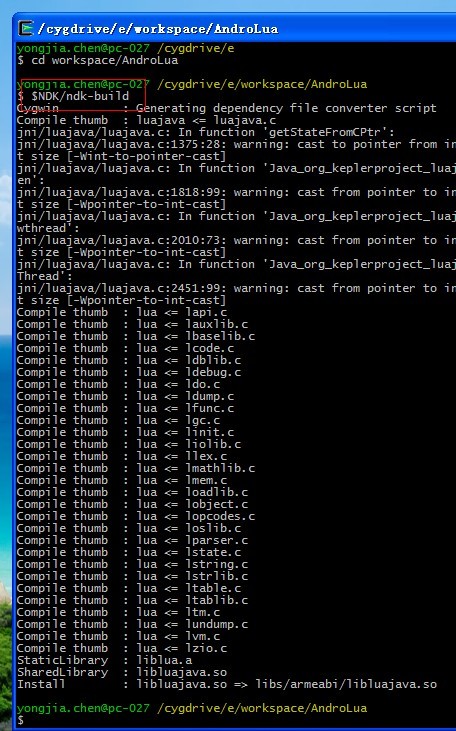
2、AndroLua项目包含了LuaJava的C源码在JNI目录中。用Android NDK编译。编译结束,在libs\armeabi目录下生成LuaJava的动态链接库文件。
编译结束。
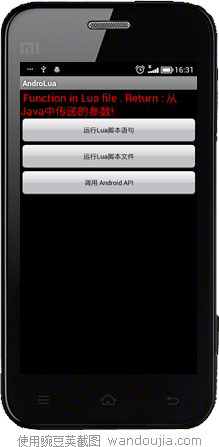
3、创建几个演示例程。这里演示三种使用Lua脚本的方式。
将上面从GitHub中克隆回来的项目导入到Eclipse中。创建一个Activity。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| public class MainActivity extends Activity { //Lua解析和执行由此对象完成 private LuaState mLuaState; //用于演示,显示数据 private TextView mDisplay; //用于演示 private LinearLayout mLayout; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); mLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.layout); mDisplay = (TextView) mLayout.findViewById(R.id.display); mLuaState = LuaStateFactory.newLuaState(); mLuaState.openLibs(); } public void runStatement(View v) { // 定义一个Lua变量 mLuaState .LdoString(" varSay = 'This is string in lua script statement.'"); // 获取 mLuaState.getGlobal("varSay"); // 输出 mDisplay.setText(mLuaState.toString(-1)); }public void runFile(View v) { mLuaState.LdoString(readStream(getResources().openRawResource( R.raw.test))); // 找到functionInLuaFile函数 mLuaState.getField(LuaState.LUA_GLOBALSINDEX, "functionInLuaFile"); // 将参数压入栈 mLuaState.pushString("从Java中传递的参数"); // functionInLuaFile函数有一个参数,一个返回结果 int paramCount = 1; int resultCount = 1; mLuaState.call(paramCount, resultCount);// 将结果保存到resultKey中 mLuaState.setField(LuaState.LUA_GLOBALSINDEX, "resultKey"); // 获取 mLuaState.getGlobal("resultKey"); // 输出 mDisplay.setText(mLuaState.toString(-1)); }public void callAndroidAPI(View v) { mLuaState.LdoString(readStream(getResources().openRawResource( R.raw.test))); // 找到functionInLuaFile函数 mLuaState.getField(LuaState.LUA_GLOBALSINDEX, "callAndroidApi"); mLuaState.pushJavaObject(getApplicationContext()); mLuaState.pushJavaObject(mLayout); mLuaState.pushString("设置到TextView的数据"); mLuaState.call(3, 0); }private String readStream(InputStream is) { try { ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); int i = is.read(); while (i != -1) { bo.write(i); i = is.read(); } return bo.toString(); } catch (IOException e) { Log.e("ReadStream", "读取文件流失败"); return ""; } }} |
//此函数由Java代码调用。接受一个参数,并返回一个字符串
function functionInLuaFile(key)
return ' Function in Lua file . Return : '..key..'!'
end
//此函数由Java代码调用。接受三个参数。并调用这些Android组件的方法。
function callAndroidApi(context,layout,tip)
//创建一个Android TextView
tv = luajava.newInstance("android.widget.TextView",context)
//调用TextView的方法
tv:setText(tip)
//调用Layout的方法
layout:addView(tv)
end
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/layout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" ><TextView android:id="@+id/display" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:id="@+id/statemanet" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:onClick="runStatement" android:text="运行Lua脚本语句" /><Button android:id="@+id/file" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:onClick="runFile" android:text="运行Lua脚本文件" /> <Button android:id="@+id/callAndroid" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:onClick="callAndroidAPI" android:text="调用 Android API" /></LinearLayout> |